
The first secretary of the U.S. Treasury, Alexander Hamilton, assumed all the debt incurred by the Revolutionary War. He then resold those debts to U.S.-speculators, promising a good yield. The proceeds of these sales were used to finance his new government. Eventually, Hamilton became the nation's first secretary of the Treasury.
Asset maturities
Asset maturities management is an important aspect of financial planning. The maturity dates of assets and liabilities determine whether they will create cash outflows or inflows. Calculating effective maturities is possible using "liquidity duration", which is the amount of time that an entity will need to dispose an instrument in a crisis. You can also use historical data to predict nonmaturity assets.
Asset management is the systematic, coordinated effort required to achieve an organisation's goals. It is a leading indicator of future performance and serves as a guide to improvement. To help you identify areas of improvement, the maturity level of a company may be compared to its target maturity.
Cash-flow mismatches
When assets and liability are not equal, this is known as a cash-flow missmatch. It can be caused, among other things, by interest rates or cash flows. Banks could be facing major difficulties if cash flows are not in line with their expectations. There are many solutions that can mitigate this risk.
Traditional portfolio management methods can reduce your exposure to rising and declining interest rates. They can also reduce seasonal exposures. They can reduce seasonal exposures. However, members often feel the effects of these measures by changing their terms for borrowing and deposit. Alternative measures such as derivatives can be less opaque.
Interest rate risk (IRR) exposures
Although the overall level of IRR exposure in banking seems to be moderate, some institutions may have higher levels. A rise in interest rates could negatively impact the net worth of more than half the eurozone banks. The overall bank's IRR exposure has decreased since the beginning, but the volume of longer-dated receiver floating switches has increased since March 2021. This suggests that euro area banks use derivatives as hedge tools. Monitoring your bank's IRR exposures is essential.
Banks must manage IRR through strong interest rate exposure management processes. These include strong corporate governance, effective risk measuring systems and internal controls. Also, consider the impact of new strategies upon your organization's IRR exposure.
Asset/liability committee (ALCO)
An asset/liability committee is the group responsible for managing a bank's assets and liabilities. Its members monitor the bank’s balance sheets and can have a major impact on its stock price and net earnings. It also reviews the bank's interest rates risk, which is part of its operating model.
The Asset/Liability Management Committee meets every other week to review and approve contingency plan approvals, examine the organization's liquidity, and manage funds. It also reviews short-term funding requirements and funds sources. It examines the company’s interest and risk-management.
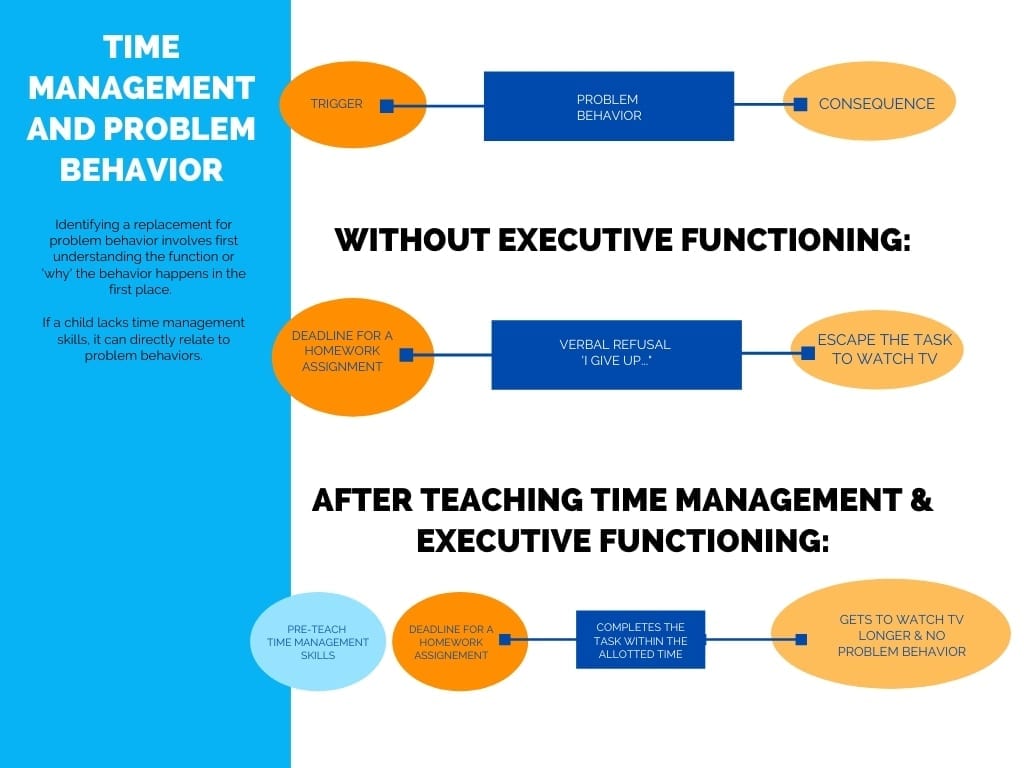
Methods
Asset liability management involves managing financial assets and liabilities. It is a multifaceted discipline. The methods employed to manage these investments have been developed by a variety of researchers. Many of them specialize in certain aspects of asset and liability management. For instance, one of the primary functions of an asset management strategy is to select a portfolio that balances the company's needs while maximizing profit.
Financial institutions are able to use sophisticated analytical tools for asset management to understand their risks and profitability better. They can help you determine the optimal balancesheet composition and asset allocation. Financial institutions can thus continue to increase their profitability and competitiveness.
FAQ
What is the difference of a program and project?
A project is temporary while a programme is permanent.
A project typically has a defined goal and deadline.
It is often performed by a team of people, who report back on someone else.
A program often has a set goals and objectives.
It is often implemented by one person.
What are the three main management styles you can use?
The three basic management styles are: authoritarian, laissez-faire, and participative. Each style has its strengths and weaknesses. Which style do YOU prefer? Why?
Authority - The leader is the one who sets the direction and expects everyone in the organization to follow it. This style works best if the organization is large and stable.
Laissez-faire – The leader gives each individual the freedom to make decisions for themselves. This style is most effective when the organization's size and dynamics are small.
Participative – The leader listens and takes in ideas from all. This approach works best in small organizations where everyone feels valued.
What are the steps of the management decision-making process?
The decision-making process of managers is complicated and multifaceted. It includes many factors such as analysis, strategy planning, implementation and measurement. Evaluation, feedback and feedback are just some of the other factors.
The key thing to remember when managing people is that they are human beings just as you are and therefore make mistakes. You can always improve your performance, provided you are willing to make the effort.
We explain in this video how the Management decision-making process works. We will explain the importance of different types decisions and how every manager can make them. The following topics will be covered.
Statistics
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How do you implement Quality Management Plans (QMPs)?
Quality Management Plan (QMP), which was introduced in ISO 9001:2008, provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products, and services through continual improvement. It emphasizes on how to continuously measure, analyze, control, and improve processes, product/service, and customer satisfaction.
QMP is a method that ensures good business performance. QMP is a standard method that improves the production process, service delivery, customer relationship, and overall business performance. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. If the QMP only covers one aspect, it's called a "Process QMP". If the QMP is focused on a product/service, it's called a QMP. QMP stands for Customer Relationships.
Two main elements are required for the implementation of a QMP. They are Scope and Strategy. These elements can be defined as follows.
Scope: This determines the scope and duration of the QMP. For example, if your organization wants to implement a QMP for six months, this scope will define the activities performed during the first six months.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP comprises five phases: Planning and Design, Development, Construction, Implementation, Maintenance. Each phase is described below:
Planning: In this stage, the objectives of the QMP are identified and prioritized. In order to fully understand and meet the needs of all stakeholders involved in this project, they are consulted. After identifying the objectives, priorities, and stakeholder involvement, the next step is to develop the strategy for achieving these objectives.
Design: This stage is where the design team creates the vision, mission and strategies necessary for successful implementation of QMP. These strategies are implemented by the development of detailed plans and procedures.
Development: Here, the team develops the resources and capabilities that will support the successful implementation.
Implementation is the actual implementation of QMP according to the plans.
Maintenance: The maintenance of the QMP is an ongoing task.
The QMP must also include several other items:
Stakeholder Involvement: Stakeholders are important for the success of the QMP. They are required to actively participate in the planning, design and development of the QMP, as well as the implementation and maintenance phases.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: It is important to consider the QMP's time frame. You can use a simplified version if you are only going to be using the QMP for short periods. If you are looking for a longer-term commitment, however, you might need more complex versions.
Cost Estimation is another important aspect of the QMP. It is impossible to plan without knowing what you will spend. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
The most important thing about a QMP is that it is not just a document but also a living document. It changes with the company. It is important to review it periodically to ensure it meets all current requirements.